Les cartes de circuits imprimés, ou PCB, constituent la base de la plupart des appareils électroniques. Ils sont fabriqués en superposant de fines feuilles de cuivre sur un substrat non conducteur, puis en éliminant l'excédent de cuivre par gravure pour créer le motif de circuit souhaité.
Les PCB peuvent être très simples, avec seulement quelques traces de cuivre, ou extrêmement complexes, avec plusieurs couches de circuits interconnectés, formant effectivement un maillage en 3D. Le processus de fabrication doit être soigneusement contrôlé afin de garantir que le PCB fini réponde aux spécifications souhaitées, sans contact manquant ou intermittent.
Plusieurs méthodes peuvent être utilisées pour créer le motif du circuit sur un PCB. Le choix de la méthode dépendra de la complexité du motif souhaité. Les méthodes les plus courantes, également utilisées dans les deux vidéos ci-dessous, pour créer des motifs de circuit sur les PCB sont la photolithographie et la gravure :
- Photolithographie est un procédé qui consiste à utiliser la lumière pour créer le motif de circuit souhaité sur le PCB. Un matériau sensible à la lumière, appelé photorésist, est utilisé pour recouvrir le circuit imprimé. Le motif souhaité est ensuite transféré sur le photorésist à l'aide d'un masque. Les zones exposées du photorésist sont ensuite développées, ce qui laisse une image négative du motif souhaité.
- Gravure : L'étape suivante consiste à graver le cuivre exposé pour créer le motif de circuit souhaité. Il existe de nombreux produits chimiques de gravure différents qui peuvent être utilisés, en fonction du type de cuivre utilisé et des résultats souhaités.
Une fois la gravure terminée, la résine photosensible restante est retirée, laissant derrière elle le motif de circuit souhaité sur le PCB, prêt pour les étapes suivantes, telles que le traitement de surface, le revêtement, le perçage et les vias.
Ces étapes sont présentées de manière beaucoup plus détaillée et expliquées dans les deux usines de fabrication de circuits imprimés ci-après, de la prise de commande au contrôle et à l'emballage, ce qui permet d'atteindre les impressionnants KPI suivants
- délai total de livraison entre la prise de commande et l'expédition : 2 à 4 jours
- Plus de 5000 commandes par jour !
et ceci pour des commandes à l'unité, pas nécessairement des clients qui reviennent, pour des pros et des non-pros - ce qui signifie des erreurs potentielles dans la demande -, et quelques contrôles de conception et de qualité au cours du processus. Soyez inspirés !
Sur PCBway:
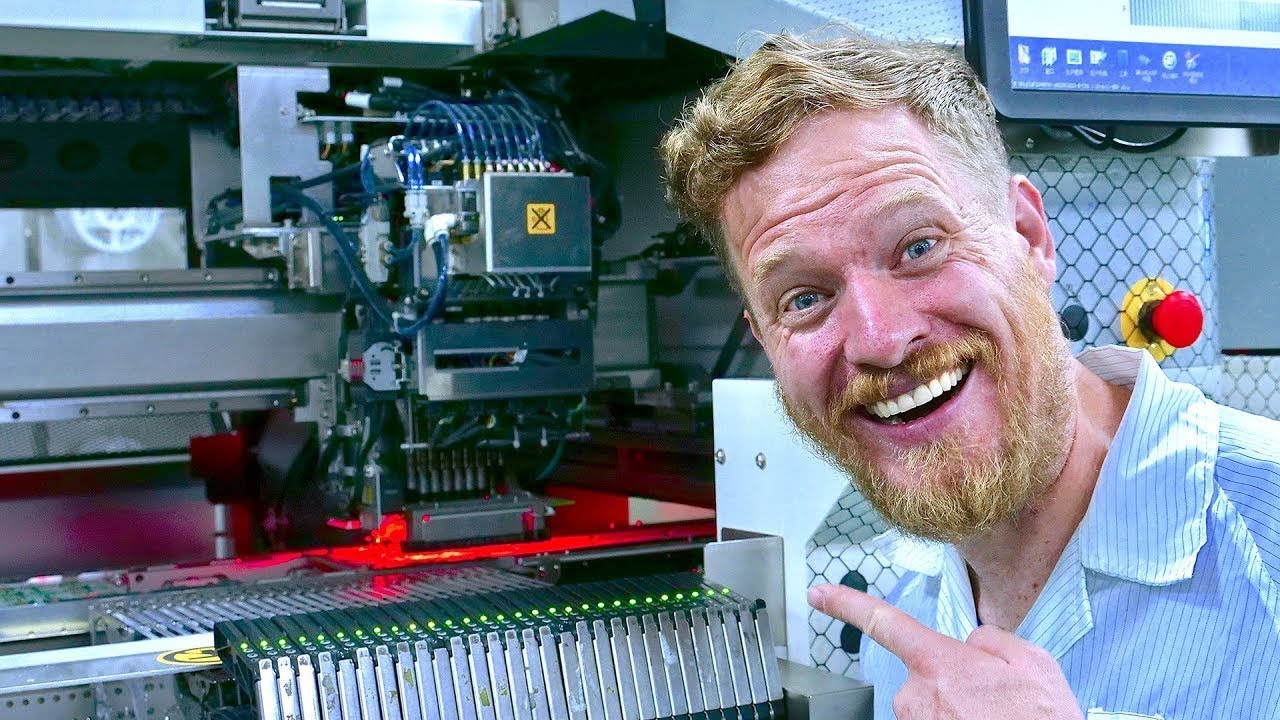

Et ensuite comment son concurrent le fait, JLCPCB
Pour plus de détails sur le vocabulaire électronique, les types de circuits imprimés et l'empreinte des composants, reportez-vous à l'article détaillé sur les circuits imprimés et l'électronique.
